When it comes to understanding your own body, knowledge is power. This is especially true when it comes to understanding your sexual anatomy as a woman. By gaining a better understanding of the various parts of your sexual anatomy, you can empower yourself to take control of your sexual health and pleasure. In this guide, we will break down the key components of a woman’s sexual anatomy and provide you with the knowledge you need to navigate your own body with confidence.
The Vulva
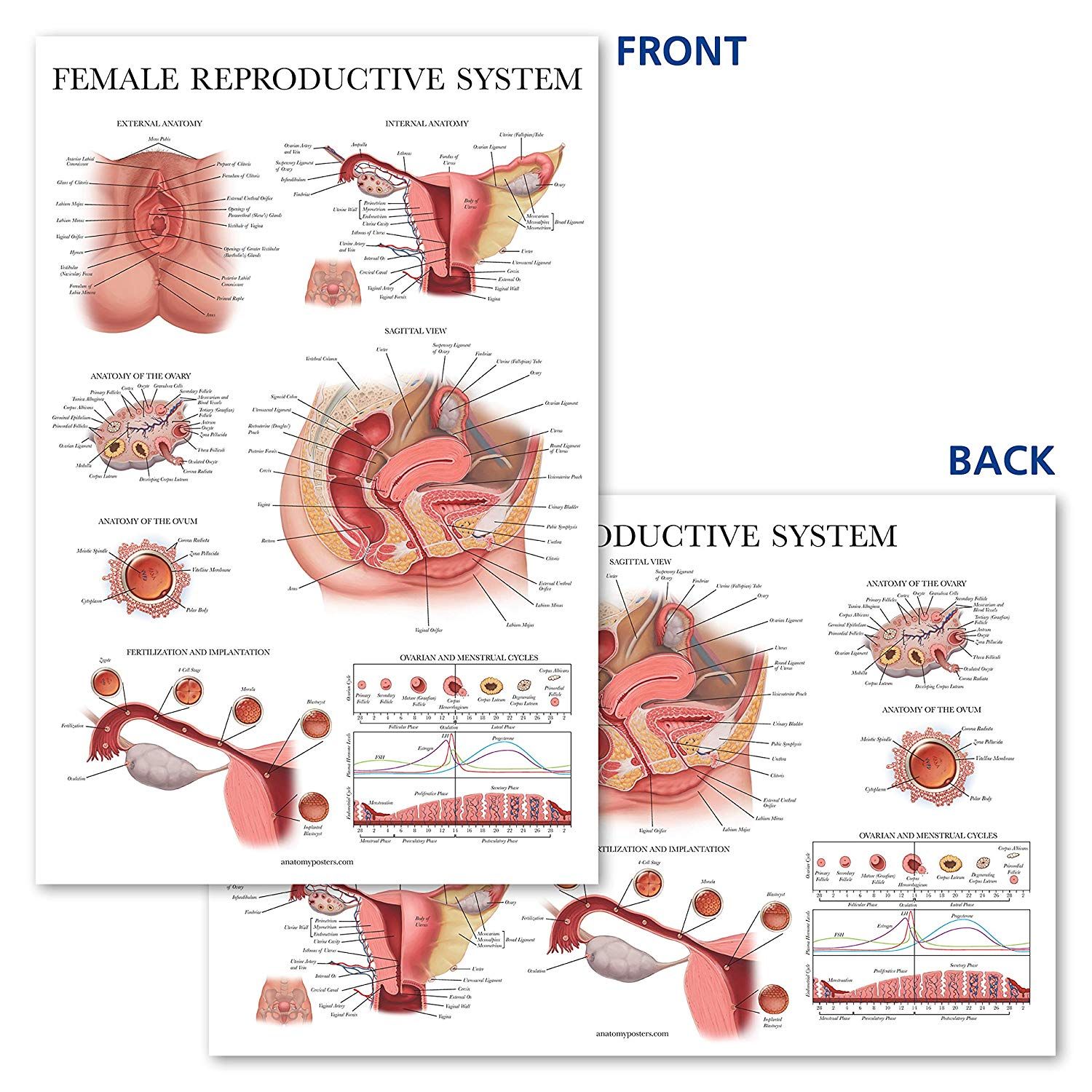
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia and is comprised of several key components. These include the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and vaginal opening. Understanding each of these parts and their functions is essential to understanding your own sexual anatomy.
Mons Pubis
The mons pubis is the rounded mound of fatty tissue that covers the pubic bone. It is typically covered in pubic hair and acts as a protective cushion for the pubic bone during sexual activity.
Labia Majora
The labia majora are the outer folds of skin that surround the vaginal opening. They are homologous to the scrotum in males and provide protection for the internal genitalia.
Labia Minora
The labia minora are the inner folds of skin that sit inside the labia majora. They contain numerous nerve endings and play a key role in sexual arousal and pleasure.
Clitoris
The clitoris is a small, sensitive organ located at the top of the vulva where the labia minora meet. It is a key player in sexual pleasure, as it contains thousands of nerve endings that make it highly sensitive to touch.
Vaginal Opening
The vaginal opening is the entrance to the vagina and is located between the labia minora. It is where penetration occurs during sexual activity, and it also serves as the exit for menstrual blood and vaginal discharge.
The Vagina
The vagina is a muscular canal that connects the external genitalia to the cervix of the uterus. It is a key component of the female reproductive system and serves several important functions. The vagina is capable of stretching and expanding to accommodate a penis or other objects during sexual activity.
The Cervix
The cervix is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It contains a small opening called the os, which allows menstrual blood to flow out of the uterus and sperm to enter during sexual intercourse. During childbirth, the cervix dilates to allow the baby to pass through the birth canal.
The Uterus
The uterus is a pear-shaped organ located in the pelvis that is responsible for housing and nourishing a developing fetus during pregnancy. It is also the source of menstrual blood during the menstrual cycle. The uterus is connected to the fallopian tubes, which transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus for fertilization.
The Ovaries
The ovaries are two small, almond-shaped organs located on either side of the uterus. They are responsible for producing eggs and hormones, including estrogen and progesterone. Each month, one of the ovaries releases an egg during ovulation, which can then be fertilized by sperm to create a pregnancy.
Conclusion
Understanding your sexual anatomy as a woman is an important step in taking control of your sexual health and pleasure. By familiarizing yourself with the key components of your sexual anatomy, you can navigate your own body with confidence and make informed decisions about your sexual and reproductive health. Remember, every woman‘s body is unique, so take the time to explore and learn what feels good for you. With knowledge and understanding, you can unlock the full potential of your sexual anatomy and enjoy a fulfilling and empowered sex life.